
ibrain
"Investigate the brain with innovative ideas for integrative understanding"
Dual goals
- To understand the biological mechanisms underlying cognition with network perspectives
- To apply acquired knowledge to translational research for neurodegenerative disease
Investigate pathophysiology and treatment modalities of disease that give perturbation to cognitive functions
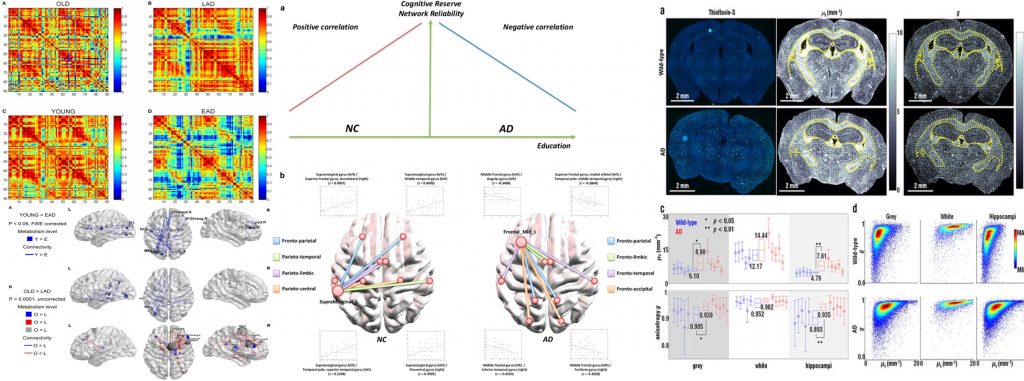
- Glucose Metabolic Brain Networks in Early-onset vs. Late-Onset Alzheimer's Disease
Front. Aging Neurosci., 2016 (Link)
- A Network flow-based analysis of cognitive reserve in normal ageing and Alzheimer's Disease
Sci Rep., 2015 (Link)
- Non-monotonic reorganization of brain networks with Alzheimer's disease progression
Front. Aging Neurosci, 2015 (Link)
- Label-free optical quantification of structural alterations in Alzheimer's disease
Sci Rep, 2016 (Link)
- Neural substrates of motor and non-motor symptoms in Parkinson's disease: a resting FMRI study
PLoS One, 2015 (Link)
Investigate pathophysiology and treatment modalities of vascular disorders that give perturbation to cognitive functions
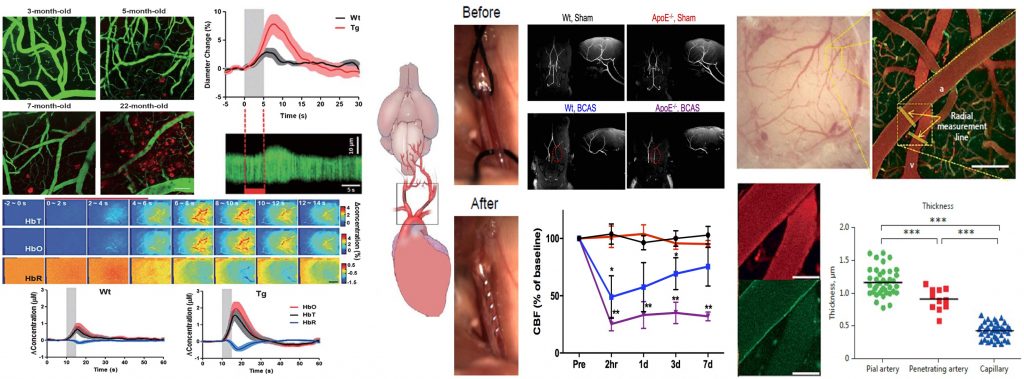
- Augmentation of sensory-evoked hemodynamic response in an early Alzheimer's disease mouse model
J. Alzheimer Dis., 2013. (Link)
- A Mouse Model of Subcortical Vascular Dementia Reflecting Degeneration of Cerebral White Matter and Microcirculation
J Cereb Blood Flow Metab, 2017 (Link)
- In vivo Imaging of the Cerebral Endothelial Glycocalyx in Mice
J Vasc Res, 2017 (Link)
- Blood Viscosity in Subcortical Vascular Mild Cognitive Impairment with versus without cerebral amyloid burden.
J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis, 2014 (Link)
- Dementia Mouse Model Atlas project http://sivd-atlas.kaist.ac.kr/
Explore the integrative nature of brain function from a micro to a large-scale network to understand higher cognitive function
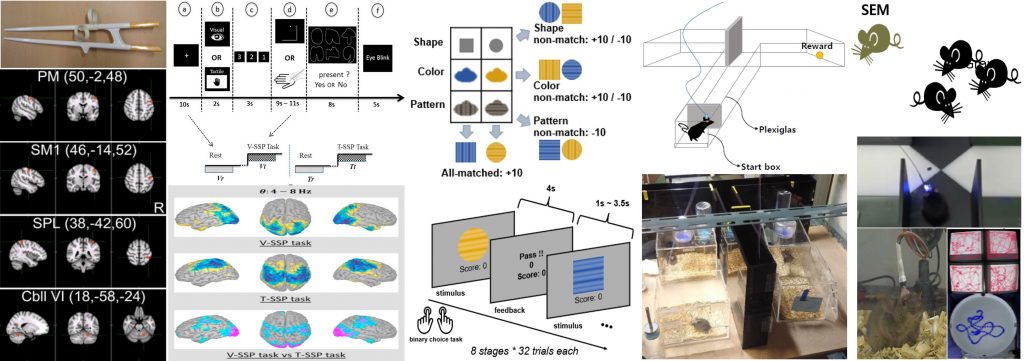
- Tool-use practice induces changes in intrinsic functional connectivity of parietal areas
Front. Neurosci, 2013. (Link)
- Modality-specific spectral dynamics in response to visual and tactile sequential shape information processing tasks: An MEG study using multivariate pattern classification analysis
Brain Res, 2016. (Link)
- Exploring Feature Dimensions to Learn a New Policy in an Uninformed Reinforcement Learning Task
Sci Rep. 2017 (Link)
- Elevated emotional contagion in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease with increased synchronization
Sci Rep, 2017 (Link)
Explore the integrative nature of brain function from a micro to a large-scale network to understand higher cognitive funtions
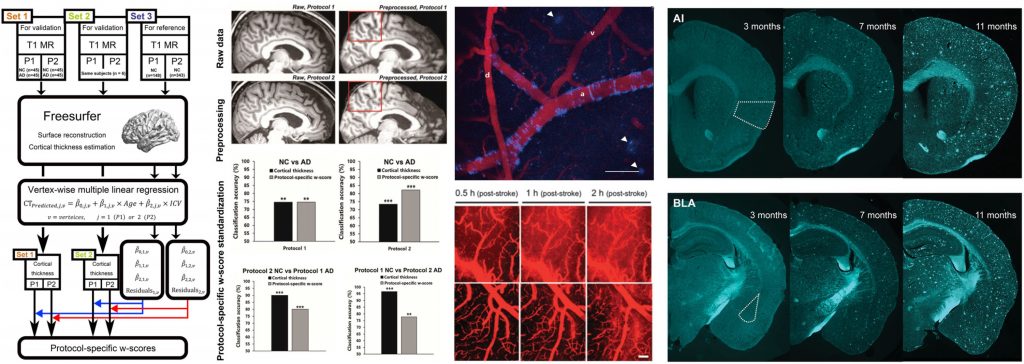
- Normalization of cortical thickness measurements across different T1 MR imaging protocols by novel W-Score standardization
Neuroimage, 2017. (Link)
- Morphological and Microstructural Changes of the Hippocampus in Early MCI: ADNI study
J. Clin Neurol, 2017. (Link)
- In vivo images of cerebral amyloid angiopathy in Alzheimer's disease mouse model
J. Stroke, 2015 (Link)
- In vivo multi-Photon luminescence imaging of cerebral vasculature and blood-brain barrier integrity using gold nanoparticles
J. Mat Chem, 2015 (Link)
- Elevated emotional contagion in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease with increased synchronization in the insula and amygdala
Sci Rep., 2017 (Link)
Study the biological mechanisms of the brain to investigate organization and function using state of the art imaging modalities
- Degree-based statistic and center persistency for brain connectivity analysis (HBM Jan 2017 Journal Cover Image)
Hum Brain Mapp., 2017. (Link)
- Sparse SPM: Group Sparse-dictionary learning in SPM framework for resting-state functional connectivity MRI analysis
Neuroimage, 2016 (Link)
- Node Identification using inter-Regional Correlation Analysis for Mapping Detailed Connections in Resting State Networks
Front. Neurosci, 2017 (Link)
- Altered intrinsic functional connectivity in the latent period epileptogenesis in a temporal lobe epilepsy model
Exp Neurol, 2017 (Link)
- Momentary level of slow default-mode network activity is associated with distinct propagation and connectivity patterns in the anesthetized mouse cortex
J Neurophysiol. 2018 (Link)
